- News and Blog
SenseTime Wins the Best Paper Award at CVPR 2023 For Groundbreaking Perception-Decision Integrated Autonomous Driving Foundation Model
June 23, 2023 – SenseTime and its joint labs were recognized for its AI research at the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR) 2023, the world’s largest annual conference on computer vision and AI. Two papers from SenseTime were included in the list of 12 award candidate papers. Among them, the research paper “Planning-oriented Autonomous Driving” won the Best Paper Award.
The CVPR is the top prestigious conference in computer vision and AI where the sharpest minds in the field showcase their cutting-edge research. CVPR 2023 was held in Vancouver, Canada from June 18th to 22nd. This year, a record number of 9,155 papers were submitted, and 2,369 papers were accepted, of which 54 papers were from SenseTime and its joint labs.
Received Best Paper Award for Research Presenting Significant Breakthrough in Autonomous Driving
Autonomous driving is a highly complex technology that requires expertise in multiple fields, such as sensor technology, machine learning, and path planning. Additionally, it is necessary to adapt to different road rules and traffic cultures and interact well with other vehicles and pedestrians to achieve reliable and safe autonomous driving systems. Given these complexities, most of the research related to autonomous driving focuses on specific modules, with discussions on framework research being relatively scarce.
The winning paper, “Planning-oriented Autonomous Driving” introduces Unified Autonomous Driving (UniAD), a comprehensive up-to-date framework that incorporates full-stack driving tasks, including detection, tracking, mapping in perception, as well as motion and occupancy forecast in prediction in one network.
Instead of a simple stack of tasks, UniAD investigates the effect of each module in perception and prediction, leveraging the benefits of joint optimization from preceding nodes to final planning in the driving scene. All perception and prediction modules are designed in a transformer decoder structure, with task queries as interfaces connecting each node. This innovative approach is a significant breakthrough in autonomous driving technology research and was recognized with the first CVPR best paper award for this field.
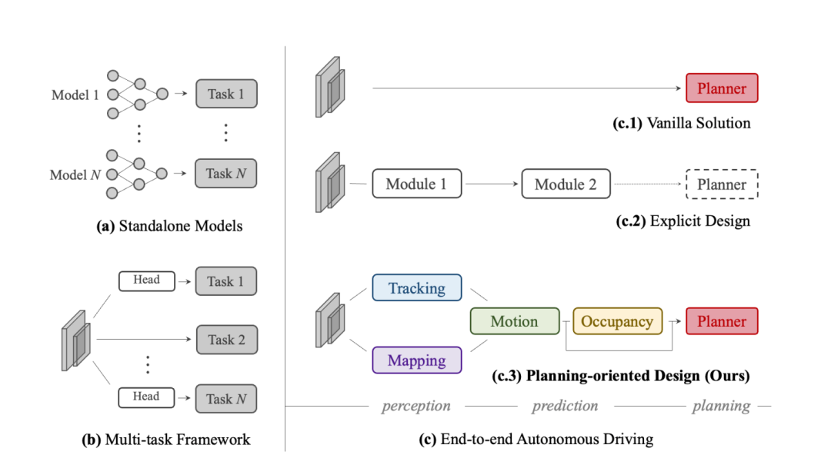
The winning paper compares various designs of autonomous driving frameworks, and argues in (c.3) that a desirable system should be planning-oriented and properly organize preceding tasks to facilitate planning.
Prof. Wang Xiaogang, Co-founder, Chief Scientist and President of Intelligent Automotive Group at SenseTime, said, “UniAD is the industry's first end-to-end autonomous driving foundation model that unites all nodes from perception and decision-making as a whole, leading to significant improvements in overall system performance and representing the forthcoming development trend of autonomous driving.”
With extensive ablations, the effectiveness of using the UniAD is proven by substantially outperforming previous state-of-the-arts (SOTA) in all aspects. For example, multi-object tracking accuracy exceeds SOTA by 20%, online mapping accuracy in lanes is increased by 30%, motion forecasting error is decreased by 38%, and planning error is reduced by 28%.
Award candidate paper: Accelerating realistic 3D content generation in the Age of AIGC
Apart from autonomous driving, the perception, understanding, reconstruction, and generation of real 3D objects is a consistently prominent issue in the field of computer vision. The award candidate paper titled “OmniObject3D: Large-Vocabulary 3D Object Dataset for Realistic Perception, Reconstruction and Generation” presents the OmniObject3D large vocabulary 3D object dataset, a large-scale collection of 6,000 high-quality real-scanned 3D objects in around 200 daily categories. Each 3D object is captured with both 2D and 3D sensors, allowing for high-quality object scans with precise shapes and realistic appearances. The resulting data includes textured meshes, point clouds, multi-view rendered images, and multiple real-captured videos.

OmniObject3D is currently the largest real-world 3D scanned model dataset in academia and provides vast opportunities for future 3D vision research. Researchers have explored its robustness and generalization of various academic tasks such as point cloud recognition, neural rendering, surface reconstruction, and 3D generation using this dataset, validating its open application prospects from perception to generation fields. With its high-quality scans, OmniObject3D is expected to play a crucial role in promoting realistic 3D generation in the AIGC era.
Moreover, SenseTime has made significant progress in various fields such as semi-supervised object detection, 3D GAN inversion framework, diffusion models, and more, which can be widely applied to content generation, 3D reconstruction, and other scenarios.
Leading Research Innovation with AI Infrastructure + Large Models
SenseTime's position as a leader in cutting-edge innovation is reinforced by investments in its AI infrastructure SenseCore and the development large models, combined with its commitment to collaborative innovation between industry, academia, and research.
“Large models are poised to revolutionize AI with their strong generalization capabilities, supported by large computing power and big data. They offer tremendous potential to understand, learn and apply knowledge in a vast array of fields, ” said Prof. Wang Xiaogang. “This will not only broaden our research horizons, but also stimulate a new round of innovation.”
Since the release of the “SenseNova” foundation model sets in early April, SenseTime has made significant progress in the development of large model, achieving breakthroughs in areas such as weather forecasting, remote sensing interpretation, and decision-making in open environments.
SenseTime looks forward to embracing and exploring major innovations brought by large models together with all sectors of industry, academia, and research, paving new directions and pathways for the forefront exploration of AI.







 Return
Return